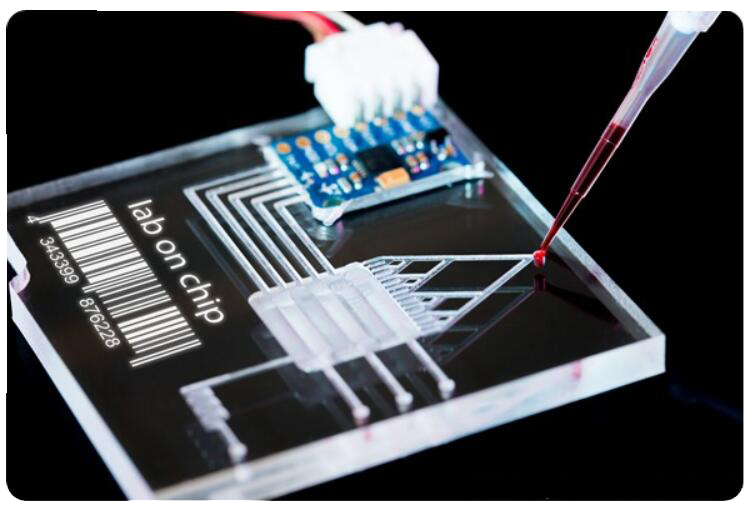
Flow cytometry has long been a cornerstone of biomedical research, enabling scientists to analyze thousands of cells in real time. From immune profiling to drug discovery, it provides a window into cellular diversity and function. Yet, as powerful as traditional cytometers are, they can be bulky, resource-intensive, and limited in flexibility. Enter microfluidics—a field that is quietly reshaping how cytometry is performed.
Microfluidics refers to the precise control of fluids at the microscale, often within chips no larger than a credit card. These chips allow researchers to manipulate cells and reagents with extraordinary accuracy, reducing sample volumes and increasing throughput. For flow cytometry, this means smaller instruments, faster results, and more reproducible data. At Creative Biolabs, we've been exploring how fabrication techniques such as micro-injection casting, laser engraving, and chip bonding can elevate microfluidic design and performance.
Why Microfluidics Matters for Flow Cytometry
Traditional cytometry setups often require large fluid reservoirs and complex optics. Microfluidic chips miniaturize these processes, enabling single-cell analysis with just microliters of sample. This efficiency not only saves time and cost but also makes cytometry more accessible for point-of-care diagnostics and portable research platforms. Imagine running a high-throughput screen in a compact device that fits on a benchtop—microfluidics makes that vision possible.
Three Fabrication Techniques That Make a Difference
Micro-Injection Casting: Precision molding replicates microfeatures with micron-level accuracy, ensuring smooth channels where cells flow without disruption. This is especially valuable for droplet-based assays, where uniformity is key.
Laser Engraving: By carving sharp, debris-free microchannels, laser engraving supports stable flow-focusing regions and reliable droplet formation. For cytometry, this translates into consistent single-cell analysis.
Microfluidic Chip Bonding: Strong seals are essential for performance. Techniques like plasma activation and thermal fusion guarantee leak-free chips that withstand high pressure while maintaining optical clarity for fluorescence detection.
Applications Beyond the Lab
The versatility of microfluidics extends far beyond cytometry. Researchers are using these chips to build organ-on-a-chip models, simulate physiological environments for drug testing, and develop rapid diagnostic tools for infectious diseases. In flow cytometry, integration with microfluidics enables high-throughput screening, single-cell genomics, and even portable devices for field research.
Looking Ahead
As microfluidics continues to evolve, its impact on cytometry will only grow. The combination of engineering precision and biological insight is reshaping how we study cells, diseases, and therapies. Future directions include integrating artificial intelligence for automated analysis, scaling up chip production for disposable diagnostics, and expanding into personalized medicine.
At Creative Biolabs, they're excited to contribute to this journey by offering fabrication services that help researchers bring their ideas to life. Whether it's casting complex geometries, engraving precise channels, or bonding durable chips, our goal is to empower innovation at the microscale.